Understanding Bacterial Skin Infections
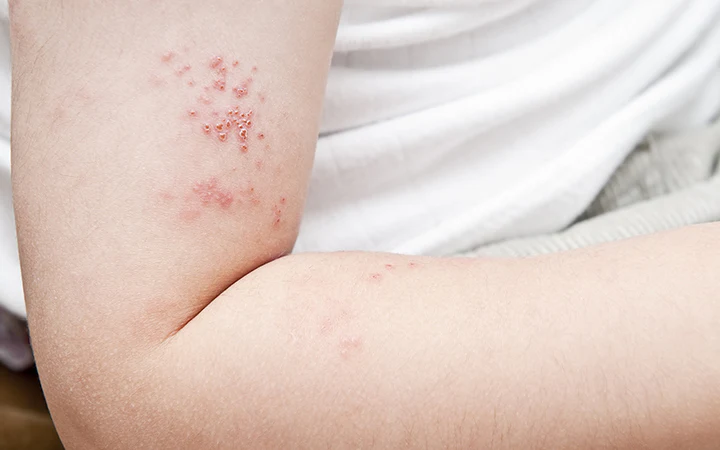
Bacterial skin infections can vary in severity and type, but they often present as red, swollen, and sometimes painful areas on the skin. Common types of bacterial skin infections include cellulitis, impetigo, and folliculitis. These infections can occur due to bacteria entering the skin through cuts, abrasions, or insect bites. Early recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent the infection from spreading and worsening.
Symptoms of Bacterial Skin Infections
The symptoms of bacterial skin infections often start with redness and warmth in the affected area. Swelling, tenderness, and pus-filled blisters may also develop. The infection can cause discomfort and may be accompanied by fever or chills, especially if it spreads to deeper layers of the skin or other parts of the body.
Causes of Bacterial Skin Infections
Bacterial skin infections are typically caused by common bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species. These bacteria can enter the skin through minor injuries, including cuts, scratches, or insect bites. Poor hygiene, weakened immune systems, and underlying health conditions can increase the risk of developing a bacterial skin infection.
The Role of Cephalexin 500Mg in Treatment
Cephalexin 500Mg is a widely used antibiotic for treating bacterial skin infections. It belongs to the cephalosporin class of antibiotics and works by inhibiting the bacteria's cell wall synthesis, leading to their destruction. Cephalexin 500Mg is effective against a broad range of bacteria and is commonly prescribed for conditions like cellulitis, impetigo, and other skin infections.
How to Take Cephalexin 500Mg
Cephalexin 500Mg is usually taken orally, with or without food, as directed by a healthcare provider. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health. It's essential to complete the full course of the antibiotic, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated and to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Additional Treatments and Care
In addition to taking Cephalexin 500Mg, keeping the infected area clean and dry is important. Applying a warm compress can help alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also be used to manage pain and fever. In some cases, topical antibiotics may be prescribed alongside oral treatment to directly target the infection site.
When to Seek Medical Help
If the infection does not improve after a few days of taking Cephalexin 500Mg, or if symptoms worsen, it's important to seek medical attention. Signs of a worsening infection include increased redness, spreading of the infection, high fever, or the development of abscesses. In such cases, a different antibiotic or additional treatments may be necessary.
Preventing Future Infections
To prevent future bacterial skin infections, practice good hygiene, keep the skin clean and moisturized, and promptly treat any cuts or injuries. Avoid sharing personal items like towels or razors, which can spread bacteria. Strengthening the immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest can also reduce the risk of infections.
Conclusion
Treating bacterial skin infections effectively involves a combination of antibiotic therapy with Cephalexin 500Mg and proper skin care. Early detection, prompt treatment, and preventive measures are key to managing these infections and preventing complications. If in doubt, always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.