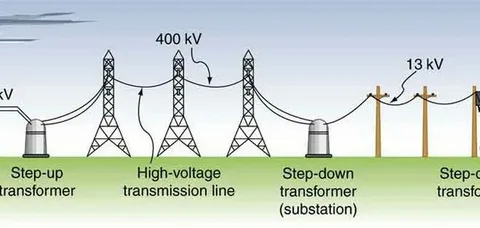
Introduction
The power transmission component market encompasses the essential hardware and systems that enable electrical energy to be transmitted from generation sources to distribution networks and end users. Components include transformers, circuit breakers, insulators, conductors, surge arresters, busbars, switchgear, connectors, and power transmission towers. As electricity demand grows and grids modernize, demand for robust, efficient, and reliable transmission components has accelerated. The market is driven by grid expansion, renewable integration, electrification of transport and industry, and the need to upgrade aging infrastructure to reduce losses and improve resilience.
Market Dynamics (Drivers, Challenges, Opportunities)
Drivers:
Several forces propel the market. First, global electrification and increasing electricity consumption—spurred by population growth, industrialization, and electrified transport—require expanded transmission capacity. Second, the integration of large-scale renewables (wind and solar) often located far from load centers demands long-distance transmission infrastructure and high-voltage equipment. Third, aging transmission networks in developed economies are prompting upgrades and replacements to prevent failures and reduce technical losses. Fourth, governments and utilities are investing in grid modernization, smart grid technologies, and high-voltage direct current (HVDC) links to increase efficiency and cross-border power trading.
Challenges:
Key challenges include the high capital expenditure required for transmission projects, lengthy permitting and right-of-way processes, and complex regulatory environments across jurisdictions. Long lead times for manufacturing large transformers and high-voltage equipment can bottleneck project timelines. The technical complexity of integrating intermittent renewables while maintaining grid stability introduces additional design and protection requirements for components. Supply chain disruption risks—material price volatility for copper, steel, and rare-earth elements, and geopolitical concentration of critical materials—can affect availability and costs. Finally, cybersecurity and physical security of grid components are increasingly important as networks become more digital and connected.
Opportunities:
Opportunities abound in advanced materials, digitalization, and new system architectures. Demand for low-loss transformers, advanced conductor technologies (ACSS, HTLS), and compact gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) is growing. HVDC systems and modular, prefabricated substation components enable faster deployment and lower footprint. Smart components with embedded sensors and condition-monitoring capabilities enable predictive maintenance and reduce unplanned outages. Emerging markets—particularly in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America—offer significant expansion potential as electrification and industrial projects accelerate. Retrofit and refurbishment services for legacy components are also a substantial market segment.
Market Segmentation
By Component Type:
- Transformers (power and distribution)
- Switchgear (air-insulated, gas-insulated)
- Circuit breakers and relays
- Conductors and overhead lines (ACSR, AAC, HTLS)
- Insulators and bushings
- Surge arresters and lightning protection
- Substation equipment (buses, disconnectors, monitoring devices)
By Voltage Level:
- Low Voltage (<1 kV)
- Medium Voltage (1–72.5 kV)
- High Voltage (72.5–230 kV)
- Extra High Voltage (>230 kV)
- Ultra High Voltage (UHV, >800 kV)
By End-User:
- Utilities & Grid Operators
- Renewable Energy (wind, solar farms)
- Industrial (mining, petrochemical, manufacturing)
- Commercial & Residential Distribution
- Transportation & Rail Electrification
By Region:
- Asia-Pacific
- North America
- Europe
- Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific is the largest and fastest-growing market, led by China and India, driven by extensive grid expansion, rural electrification, and rapid renewable deployment. Massive investments in ultra-high-voltage (UHV) and inter-regional transmission projects underpin demand for transformers, conductors, and GIS. North America focuses on grid modernization, smart substations, and replacing aging equipment; the U.S. sees growth in transmission upgrades and long-distance HVDC to connect renewables. Europe emphasizes decarbonization, cross-border interconnectors, and distribution automation—spurring demand for low-loss transformers, flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS), and advanced switchgear. Middle East & Africa investments are concentrated in power capacity expansion and oil & gas electrification projects, while Latin America projects are driven by hydro and renewables-linked transmission initiatives.
Key Trends
- Digitalization & Smart Components: Embedded sensors, IEC 61850 communications, and condition monitoring across transformers and switchgear enable predictive maintenance and grid analytics.
- HVDC & Long-Distance Links: HVDC lines and converter stations are favored for efficient long-distance and undersea transmission of renewable power.
- Low-Loss & Eco-Friendly Equipment: Energy-efficient transformers (Amorphous core, low-loss designs) and non-toxic insulating media (synthetic ester fluids vs mineral oil, SF6 alternatives) are gaining traction.
- Compact, Modular Substations: Prefabricated, modular substations and GIS allow rapid deployment in space-constrained or urban environments.
- Advanced Conductors & Line Technologies: High-temperature low-sag (HTLS) and Aluminium Conductor Steel Supported (ACSS) conductors increase capacity without replacing towers.
- Resilience & Cybersecurity: Hardened components, redundancy, and improved cybersecurity practices for digital protection relays and substation control systems.
Future Outlook
The power transmission component market is expected to grow strongly as nations invest to meet electrification, renewable integration, and resilience goals. Technological advancements—especially in HVDC, smart sensors, and low-loss equipment—will reshape procurement patterns and lifecycle economics. Asia-Pacific will continue to dominate volume demand, while Europe and North America will push higher-value, technology-intensive solutions. Markets for retrofits, spares, and aftermarket services will expand alongside primary equipment sales. Policy clarity, financing mechanisms for grid projects, and progress in sustainable insulating gases and materials will influence the pace of adoption.
Conclusion
Power transmission components form the backbone of modern electric systems, enabling efficient delivery of electricity from generators to consumers. As the energy transition accelerates, demand for advanced, low-loss, digitally enabled, and resilient transmission hardware will rise. Manufacturers and utilities that prioritize innovation, sustainability, and digital integration will be best positioned to capture growth in both developed and emerging markets.